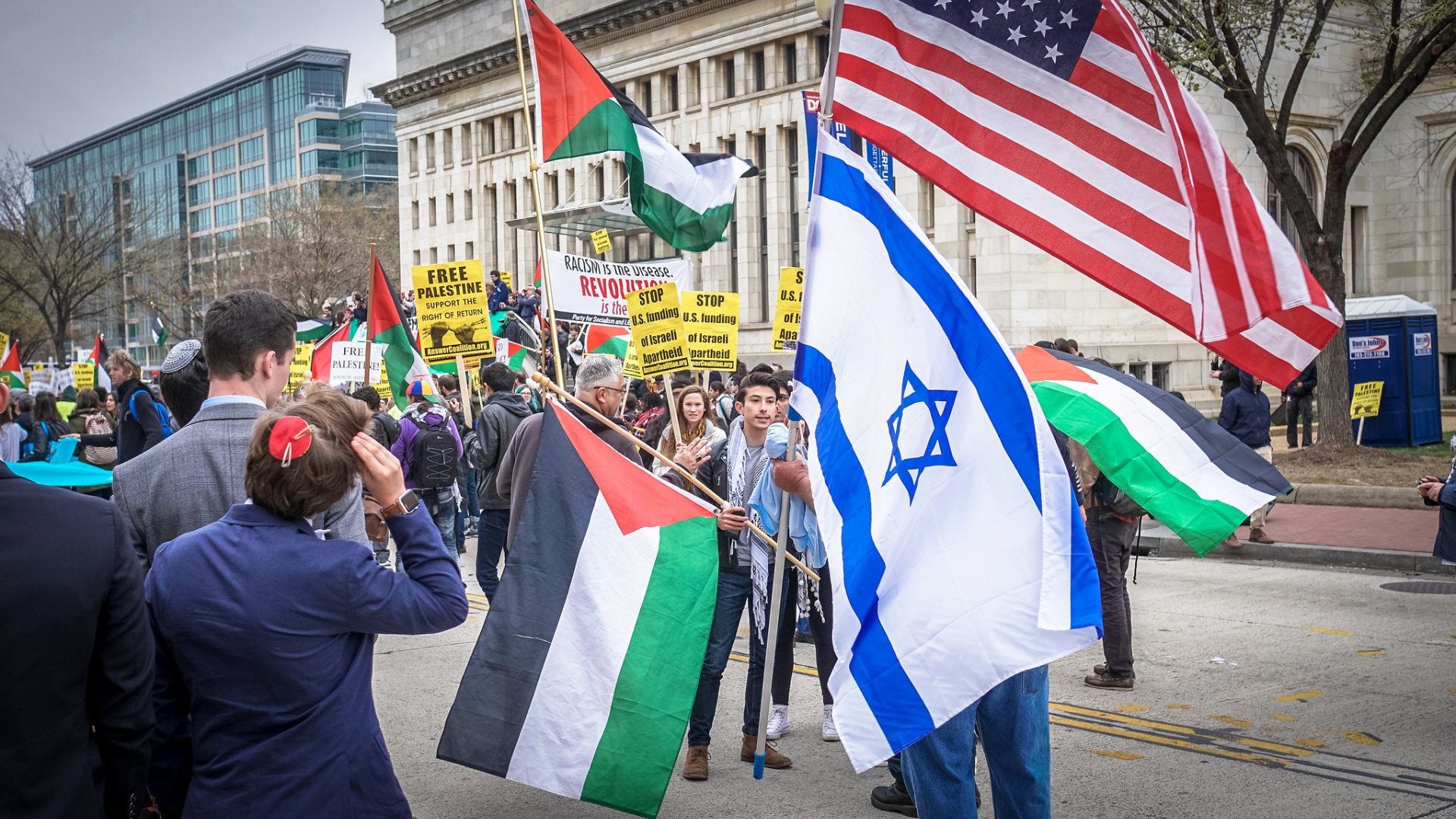
The ongoing cease-fire negotiations between Israel and Hamas are a testament to the complexities inherent in Middle Eastern diplomacy. The U.S.-proposed framework, aimed at halting hostilities in Gaza, underscores the delicate balance required to address the conflicting interests of both sides. However, significant obstacles remain unresolved, including the withdrawal of Israeli forces from Gaza, the release of hostages, and the management of the Philadelphi Corridor. These challenges not only highlight the intricate nature of the cease-fire negotiations but also reflect the broader geopolitical dynamics at play.
The cease-fire negotiations between Israel and Hamas are emblematic of the broader challenges facing Middle Eastern diplomacy. The U.S.-proposed framework, while comprehensive, faces significant hurdles in its implementation, particularly regarding the withdrawal of Israeli forces, the release of hostages, and the management of the Philadelphi Corridor.
Balancing Competing Interests
The United States has put forward a cease-fire proposal that it claims takes into account the interests of both Israel and Hamas. This framework includes a six-week cease-fire, the release of Israeli hostages and Palestinian detainees, and the withdrawal of Israeli forces from major population centers in Gaza. U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken, in his diplomatic shuttle between Israel, Egypt, and Qatar, has been instrumental in pushing for this agreement. However, the proposal has been met with skepticism, particularly from Hamas, which accuses the U.S. of favoring Israeli demands .
Sticking Points: Unresolved Issues
One of the most contentious issues in the negotiations is the withdrawal of Israeli forces from Gaza, particularly from the Philadelphi Corridor, a narrow strip along the Gaza-Egypt border. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has insisted on maintaining a military presence in this area to prevent weapons smuggling from Egypt into Gaza. Hamas, on the other hand, demands a full withdrawal, viewing the continued Israeli presence as an occupation. The U.S. has attempted to mediate by proposing a phased withdrawal, with the eventual establishment of an Arab security force to manage the corridor. However, this compromise has yet to satisfy either side, with Netanyahu publicly stating that Israel will not back down on this issue .
The release of hostages remains another significant hurdle. While Israel has agreed to release hundreds of Palestinian prisoners in exchange for the release of Israeli hostages held by Hamas, there is still disagreement over the specifics of this exchange. The challenge lies in ensuring that both sides adhere to the agreement without using the initial cease-fire as an opportunity to regroup and rearm. The United States has proposed a phased approach to the release of hostages, but the details of this plan remain a point of contention .
Role of External Actors: Egypt and Qatar
Egypt and Qatar have played crucial roles as mediators in the cease-fire negotiations. Egypt, in particular, has a vested interest in the outcome, given its border with Gaza and the potential for instability to spill over into the Sinai Peninsula. However, Egypt has also made it clear that it will not accept an Israeli military presence along its border. This position has added another layer of complexity to the negotiations, as any agreement must balance Egypt's security concerns with Israel's insistence on controlling the Philadelphi Corridor .
Qatar, for its part, has served as a key interlocutor with Hamas, leveraging its influence over the group to push for a cease-fire. However, Qatar's alignment with Hamas has also led to tensions with the U.S. and Israel, particularly as it tries to mediate while maintaining its relationship with the militant group. The success of the cease-fire negotiations may ultimately hinge on Qatar's ability to convince Hamas to compromise, particularly on issues like the Philadelphi Corridor and the release of hostages .
Geopolitical Implications
The cease-fire negotiations are not just about ending the immediate conflict in Gaza; they also have broader geopolitical implications. The outcome of these talks could set the stage for future negotiations on a more permanent solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Moreover, the involvement of regional powers like Egypt and Qatar underscores the importance of broader Middle Eastern dynamics in shaping the outcome of the negotiations. A successful cease-fire could potentially pave the way for further normalization of relations between Israel and Arab states, particularly Saudi Arabia, which has signaled its willingness to move forward with normalization if a pathway to Palestinian statehood is included in the deal .
The success of the cease-fire agreement will depend on the ability of all parties to compromise on these critical issues. The stakes are high, not just for Israel and Hamas, but for the broader region, where the outcome of these negotiations could have far-reaching implications for future peace and stability.